

The IPv6 subnet size is standardized by fixing the size of the host identifier portion of an address to 64 bits. It simplifies processing of packets in routers by placing the responsibility for packet fragmentation into the end points. It simplifies aspects of address configuration, network renumbering, and router announcements when changing network connectivity providers. In addition to offering more addresses, IPv6 also implements features not present in IPv4.
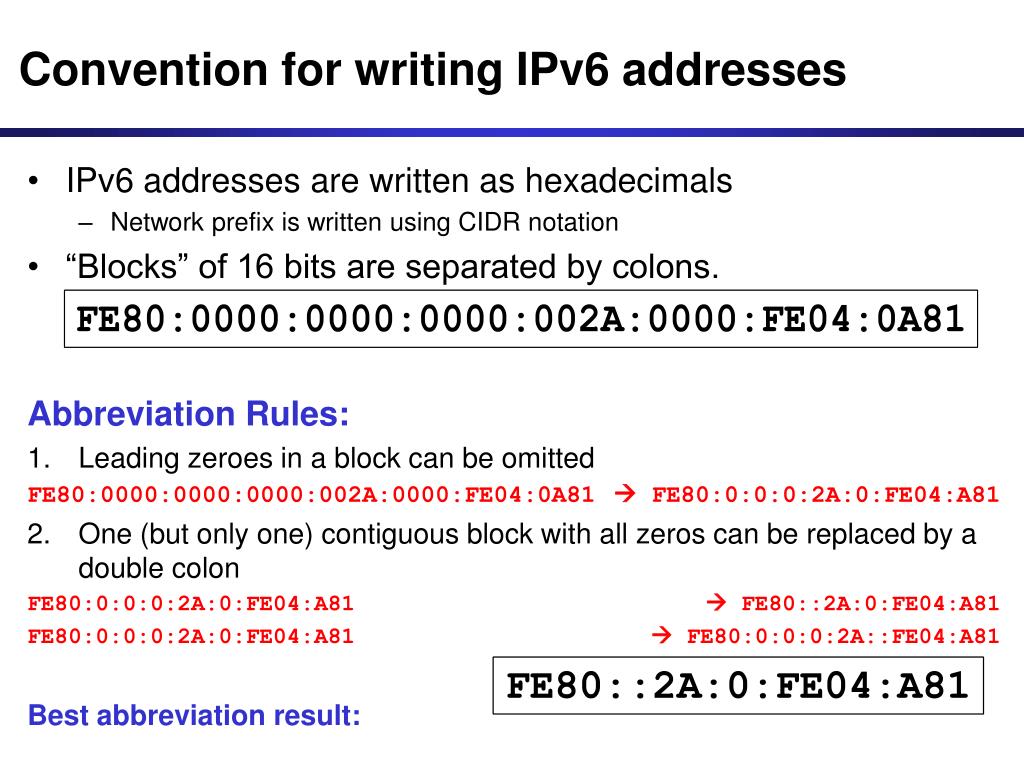
IPv6 is an Internet Layer protocol for packet-switched internetworking and provides end-to-end datagram transmission across multiple IP networks, closely adhering to the design principles developed in the previous version of the protocol, Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4). Main features Glossary of terms used for IPv6 addresses IPv6 addresses are represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits each, separated by colons. Device mobility, security, and configuration aspects have been considered in the design of the protocol. The use of multicast addressing is expanded and simplified, and provides additional optimization for the delivery of services. In particular, it permits hierarchical address allocation methods that facilitate route aggregation across the Internet, and thus limit the expansion of routing tables.

IPv6 provides other technical benefits in addition to a larger addressing space. However, several transition mechanisms have been devised to rectify this. The two protocols are not designed to be interoperable, and thus direct communication between them is impossible, complicating the move to IPv6. The actual number is slightly smaller, as multiple ranges are reserved for special use or completely excluded from use. IPv6 uses 128- bit addresses, theoretically allowing 2 128, or approximately 3.4 ×10 38 total addresses. By 1998, the IETF had formalized the successor protocol.

With the rapid growth of the Internet after commercialization in the 1990s, it became evident that far more addresses would be needed to connect devices than the IPv4 address space had available. ĭevices on the Internet are assigned a unique IP address for identification and location definition. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, which subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and was intended to replace IPv4. Internet Protocol version 6 ( IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
